实际的含权贸易中,往往包含了一些奇异的条件。而在我们持有头寸的时候,往往需要用场内标准的期权来进行对冲,通过这样的方式来减少风险。
例如我们买入一个如下条件的白糖场外期权
看跌期权, 当前价格5700, 执行价格5650, 到期日t 40交易日 波动率 0.0063, 权利金50
通过计算得知,我们的预期利润为:
期望利润: 15.662175 方差: 110.78011080184643 夏普比: 0.3548628627350025
# 蒙特卡洛算法计算期权
def SimulatePrice(P0, std, steps, step_price=1, N=10000):
"""
:param P0: 初始价格
:param std: 序列标准差
:param steps: 序列步数
:return:
""" sim_norm_ret = np.random.normal(0, std, (steps, N))
sim_price = np.exp(sim_norm_ret.cumsum(0))
# # 初始价格1000
sim_price = P0 * sim_price
sim_price = (sim_price / step_price).round(0) * step_price
# 第一行添加初始价格
sim_price = np.vstack([P0 * np.ones(N), sim_price])
return sim_price
s = 0.0063
P0 = 5700
strike_price = 5650
profit = 50
t = 40
N = 40000
# 采用蒙特卡洛方式定价
sim_price = SimulatePrice(P0, s, 40, N=N)
last_sim_price = sim_price[-1,:]
last_sim_profit = np.maximum(0, strike_price-last_sim_price) - profit
print("期望利润:", last_sim_profit.mean(), "方差:", last_sim_profit.std(), "夏普比:", last_sim_profit.mean()/last_sim_profit.std() * np.sqrt(252/t))
>期望利润: 15.662175 方差: 110.78011080184643 夏普比: 0.3548628627350025
场内期权对冲
虽然买入这样的看涨期权,期望收益是正的,但是方差太大,夏普比过低。
为了转移风险,我们可以在场内卖出一个看跌期权与我们的头寸进行对冲。 但是场内期权与我们头寸 到期日不同,执行价不同,所以我们需要构建一个头寸组合来实现我们的对冲策略。
from scipy.stats import norm
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def CND(X):
return norm.cdf(X)
# 当前期权理论价格
def PutOptionPriceBSAarry(S, K, std, t, r=0.0):
d1 = (np.log(np.divide(S , K)) + (r + (std ** 2) / 2) * t) / (std * np.sqrt(t))
d2 = d1 - std * np.sqrt(t)
return K * np.exp(-r * t) * CND(-d2) - S * CND(-d1)
index = 1
hold_position = 1
position_profit = (put_option_theory_price[index] - put_option_theory_date_price[:,index])
last_sim_price = sim_price[-1,:]
last_sim_price.resize((N,1))
put_option_theory_date_price = PutOptionPriceBSAarry(last_sim_price, strike_price_array, s, all_t-t)
p = last_sim_profit +position_profit * hold_position
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 6))
plt.subplot(1, 3, 1)
_ = plt.hist(last_sim_profit)
plt.subplot(1, 3, 2)
_ = plt.hist(position_profit)
plt.subplot(1, 3, 3)
_ = plt.hist(p)
print("期望利润:", p.mean(), "方差:", p.std(), "夏普比:", p.mean()/p.std() * np.sqrt(252/t))
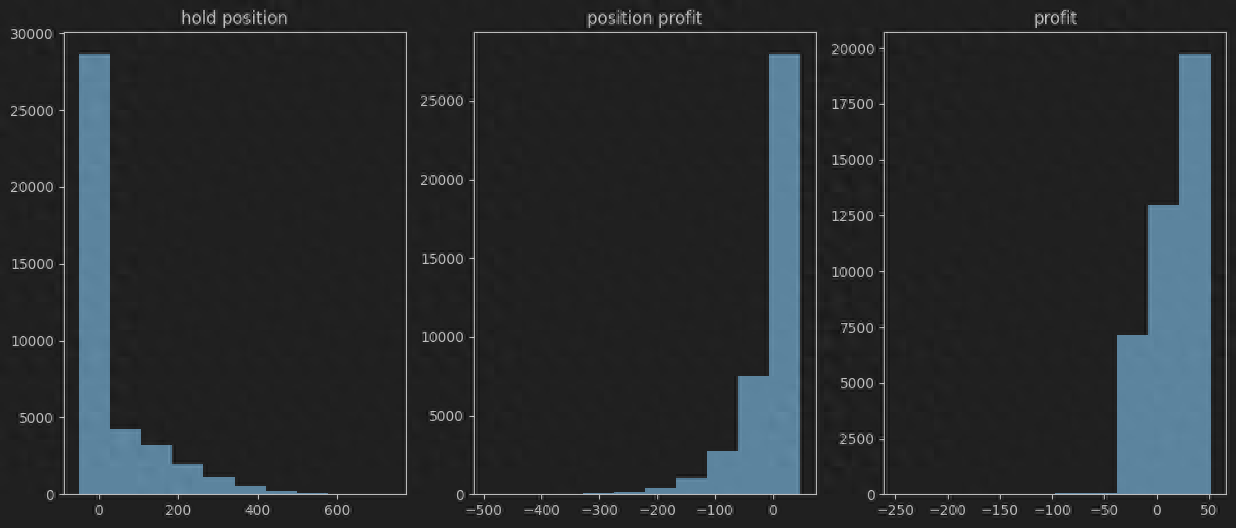
我们发现,通过构建一定比例的卖出看跌期权,夏普比明显增加!接下来我们自然的想到,如果我们把所有的场内期权都考虑进去,构建一个综合的场内期权组合,能不能尽可能的提升我们的夏普比?
构建场内期权组合
遗传算法
当前白糖2501,执行价在5000-7000之间。所以我们有20个目标期权合约,每一个期权我们都可以做多做空10手,所以我们需要构建一个投资组合。这个组合的空间是 20^20 次方,这是一个天文数字,显然遍历算法在这种复杂度面前显得力不从心。因此,我们需要一种更为高效的搜索算法来优化我们的对冲策略。这时,遗传算法便显示出它的优势。
遗传算法是一种模拟自然界生物进化过程的搜索算法,它通过种群、交叉、变异和选择等机制,不断迭代优化,最终找到问题的最优解或近似最优解。在这种背景下,我们将利用遗传算法来构建一个优化的期权对冲策略。
代码
采用Deap库,核心代码如下
invalid_ind = [ind for ind in population if not ind.fitness.valid]
fitnesses = toolbox.map(toolbox.evaluate, invalid_ind)
for ind, fit in zip(invalid_ind, fitnesses):
ind.fitness.values = fit
hof = tools.HallOfFame(10, similar=np.array_equal)
record = stats.compile(population) if stats else {}
logbook.record(gen=0, nevals=len(invalid_ind), **record)
print(logbook.stream)
ngen = 4000
cxpb = 0.5
mutpb = 0.4
# Begin the generational process
for gen in range(1, ngen + 1):
# Select the next generation individuals
offspring = toolbox.select(population, len(population))
# Vary the pool of individuals
offspring = varAnd(offspring, toolbox, cxpb, mutpb)
# Evaluate the individuals with an invalid fitness
invalid_ind = [ind for ind in offspring if not ind.fitness.valid]
fitnesses = toolbox.map(toolbox.evaluate, invalid_ind)
for ind, fit in zip(invalid_ind, fitnesses):
ind.fitness.values = fit
# Update the hall of fame with the generated individuals
hof.update(offspring)
# Replace the current population by the offspring
population[:] = offspring
population.extend(hof[:])
# Append the current generation statistics to the logbook
if gen % 10 == 0:
record = stats.compile(population) if stats else {}
logbook.record(gen=gen, nevals=len(invalid_ind), **record)
print(logbook.stream)
迭代4000次后,我们看到结果一次一次变好:
gen nevals avg std min max
0 300 0.0158112 0.0411533 -0.0391251 0.166319
10 236 0.0225989 0.0486477 -0.0387088 0.228412
20 274 0.0281336 0.0559149 -0.0384535 0.267623
30 317 0.030553 0.0709356 -0.0378094 0.522369
40 360 0.0385255 0.0961397 -0.0372828 0.894421
50 367 0.0420082 0.0887721 -0.0369026 0.894421
60 426 0.0461076 0.0955755 -0.0365466 0.923084
结果展示
param = hof[0]
option_profit_array = np.dot((put_option_theory_price-put_option_theory_date_price) ,param)
profit = last_sim_profit + option_profit_array
_ = plt.hist(profit)
print("期望利润:", profit.mean(), "方差:", profit.std(), "夏普比:", profit.mean()/profit.std() * np.sqrt(252/t))
> 期望利润: 17.317512936314248 方差: 19.143960222674735 夏普比: 2.2705131014072704
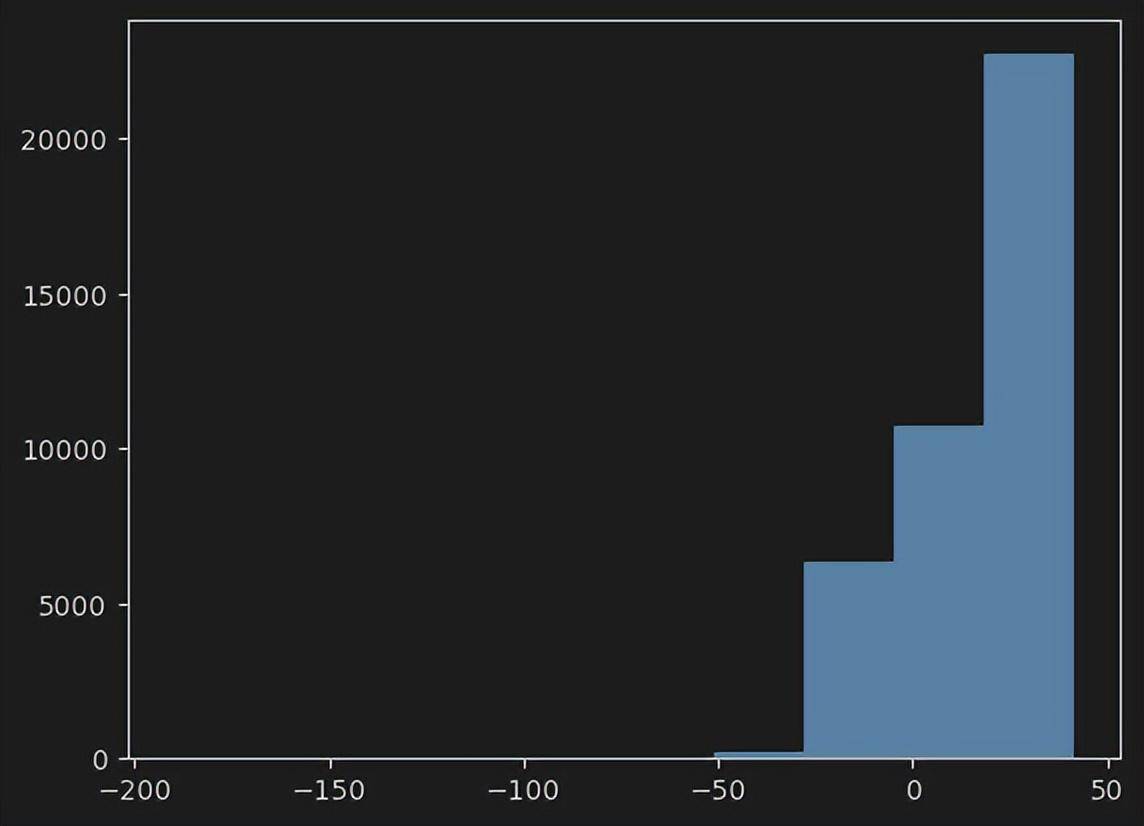
最终的夏普比为2.27。
结语
通过上面的组合,我们发现最终可以使用遗传算法模拟的组合来显著的降低风险,增加夏普比例。但是在实际交易过程中还有很多要素需要考虑,比如:
- 期现价差
- 构建组合资金占用
本文展示了如何利用遗传算法构建一个优化的期权对冲策略,显著提升了夏普比,为含权贸易的风险管理提供了新的思路。在真实的交易场景中,我们不仅要考虑策略的理论效益,更要关注其可行性和实用性。
未来,我们可以进一步研究如何将此模型应用于更多种类的期权和更复杂的交易策略中,以适应不断变化的市场环境。同时,考虑到交易成本、流动性以及模型风险等因素,不断优化策略,以实现风险与收益的最优平衡。
发布者:股市刺客,转载请注明出处:https://www.95sca.cn/archives/129446
站内所有文章皆来自网络转载或读者投稿,请勿用于商业用途。如有侵权、不妥之处,请联系站长并出示版权证明以便删除。敬请谅解!






