由于因子挖掘对于量化投资非常重要,因此本周开始,自研“因子挖掘流水线”。
1、拆解deap和gplearn代码,自研因子挖掘框架。
2、写因子挖掘的专栏系列教程。

我们需要一种符合因子表达式语法的树:
先看下效果:
随机生成一些因子:
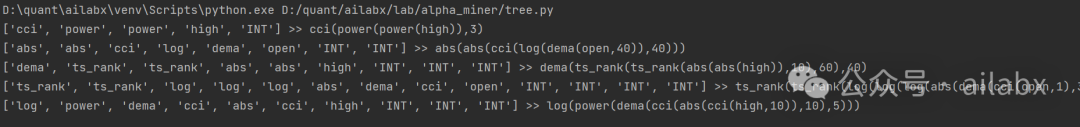
代码并不复杂:
这里对于“堆栈”的理解要比较深刻——核心逻辑,先“压栈”一个表达式,而后根据它的参数列表,比如log(EXPR),有一个参数是EXRP,再把EXPR压栈,当表达式达到预定高度时,只选择叶子节点(open,high)这种没有参数,也就是树不再生长了;还有一种情况就是常数的情况,目前就是INT,也是没有参数,自然也不再生长了。
一个while循环搞定因子生成——当然这里是随机生成。
stack = [ExprType.EXPR] expr = [] while len(stack) > 0: type_ = stack.pop() if len(expr) > self.depth and type_ == ExprType.EXPR: node = random.choice(leafs[type_]) else: node = random.choice(expr_sets[type_]) expr.append(node) for arg in reversed(node.args): stack.append(arg) return expr
也就是数据结构里用数组来实现二叉树——完整代码如下:(更完整的在星球更新:AI量化实验室——2024量化投资的星辰大海)
import random
from alpha_miner.expression import * from alpha_miner.expression import ExprType def _random_int_(): return random.choice([1, 3, 5, 10, 20, 40, 60]) class Tree: def __init__(self, min_: int, max_: int): self.depth = random.randint(min_, max_) def build(self): stack = [ExprType.EXPR] expr = [] while len(stack) > 0: type_ = stack.pop() if len(expr) > self.depth and type_ == ExprType.EXPR: node = random.choice(leafs[type_]) else: node = random.choice(expr_sets[type_]) expr.append(node) for arg in reversed(node.args): stack.append(arg) return expr def expr_to_string(self, nodes: list): string = "" stack = [] for node in nodes: stack.append((node, [])) # node和节点压进去 while len(stack[-1][1]) == stack[-1][0].arity: # 当前节点的元数 node, args = stack.pop() if len(args): string = '{}({})'.format(node.name, ','.join(args)) else: if node.type_ == ExprType.INT: string = str(_random_int_()) else: string = node.name if len(stack) == 0: break # If stack is empty, all nodes should have been seen stack[-1][1].append(string) return string if __name__ == '__main__': tree = Tree(3, 8) for i in range(5): expr = tree.build() show_name = [n.name for n in expr] print(show_name, '>>', tree.expr_to_string(expr))
第二部分的代码,是把node列表,生成一个符合咱们阅读习惯,且可以被eval的python字符串表达式:
也是类似的原理,依次入栈,当前节点的args与堆栈中一致时,出栈。
比如log(open), log先入栈,遇到open时,参数是零,直接生成字符串‘open’入log节点的栈,这时满足log节点的出栈标准,生成字符串log(open),依次类推。
这个代码还是非常有意思,非常精炼的。
下一步,我们来实现遗传算法的——复制、交叉、变异。
复制最简单——就是直接复制。
# 复制就是直接复制 def reproduce(self): return copy(self.nodes)
发布者:股市刺客,转载请注明出处:https://www.95sca.cn/archives/134172
站内所有文章皆来自网络转载或读者投稿,请勿用于商业用途。如有侵权、不妥之处,请联系站长并出示版权证明以便删除。敬请谅解!






![[通达信指标]分享一款经典公式 主力雷达](https://95sca.cn/2024/08/07/CdrQRd7uCUaF5hw1722997873.3702164.jpg?imageMogr2/thumbnail/!480x300r|imageMogr2/gravity/center/crop/480x300)